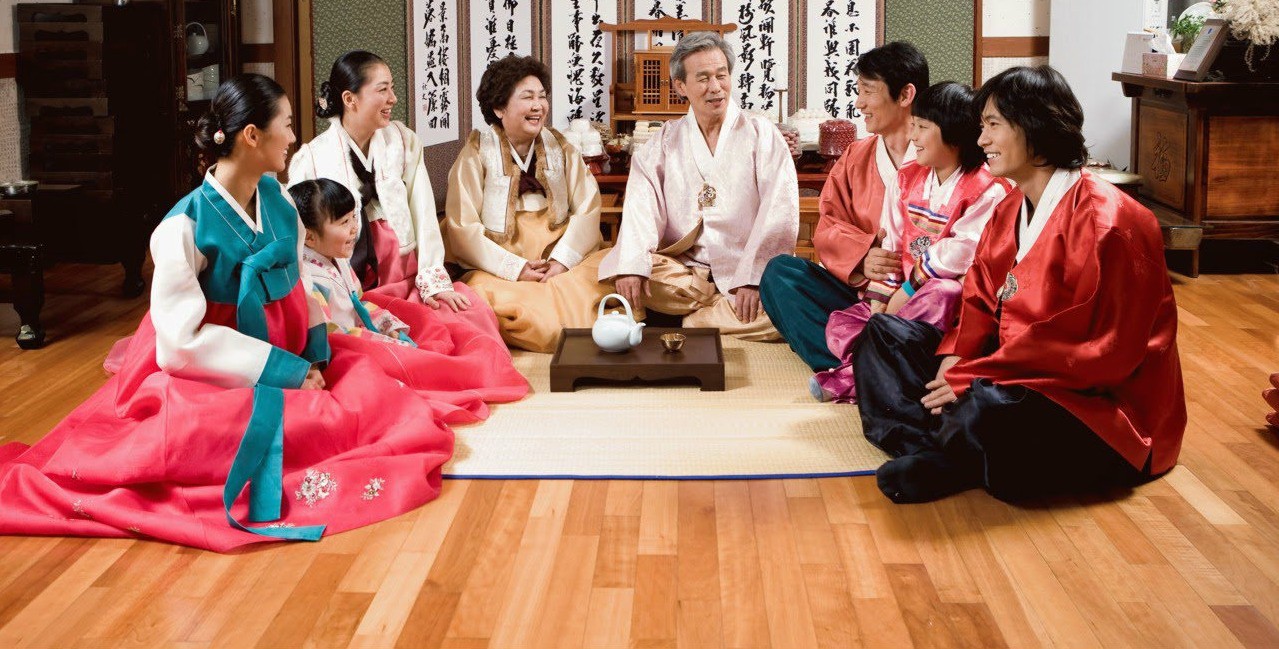
Family has a great influence and is important in shaping an individual’s personality and it sets cultural standards. Family is the basic unit of society, influencing the socialization process. In the past, in Korea, the typical family was a large family with many generations living together. Such a family would be strong and secure enough to support each other and cope with the natural and social environment. With the traditional principle of valuing family, the extended family is the first place Koreans return to when facing difficulties.

The social context of Korea affects familism:
+ Society needs a large labor force to meet the country’s industrialization and modernization process;
+ Use values and ethical standards to govern;
+ Use familism to maintain social order;
+ Promote the word “filial piety” to the national level.
– Characteristics of familism in Korea:
+ Individuals cannot be separated from their families and the relationships between family members are arranged in a very clear, tight, and strict hierarchy;
+ The family has a tradition that all family members through generations care about preserving;
+ The family becomes the most important organizational model, its influence is not only limited to blood relatives but also spreads to the whole society
Functions of the family:
+ Giving birth and raising children. From there, it plays a role in creating a labor force for society;
+ Gender control, creating balance for the marriage system;
+ Emotional exchange between family members; specific role division: men have the responsibility to do economic work, women raise children (in modern society, this has changed). Children are educated according to the Confucian ideology of loyalty and filial piety, after growing up, children must be responsible for supporting the family. The family worships ancestors.
+ The family plays a role in the socialization process: expanding to 3 areas: business, society, and the nation.
Products of familyism:
+ Hierarchy: The main relationship in the family is the relationship of superiors and subordinates according to rank and age. In a traditional Korean family, the father is the head of the family, has prestige and is respected by all. Family hierarchy is maintained by absolute obedience to superiors: children obey their parents, wives obey their husbands, younger siblings obey their elders, etc. Therefore, once the family is the most respected unit in society, family hierarchy expands into social hierarchy.
+ Familyism and family hierarchy also lead to the habit of distinguishing between relatives and strangers, near and far in all social relationships, creating networks of relationships in the form of groups and associations.
Ideas in Korean families:
+ “One becomes an official, the whole family benefits”, not causing loss of face to the family, neighbors, etc.
+ Loyalty ideology: Society forms vertical relationships (protection, group interests, blood relations); there is no diversity and breakthrough in thinking.
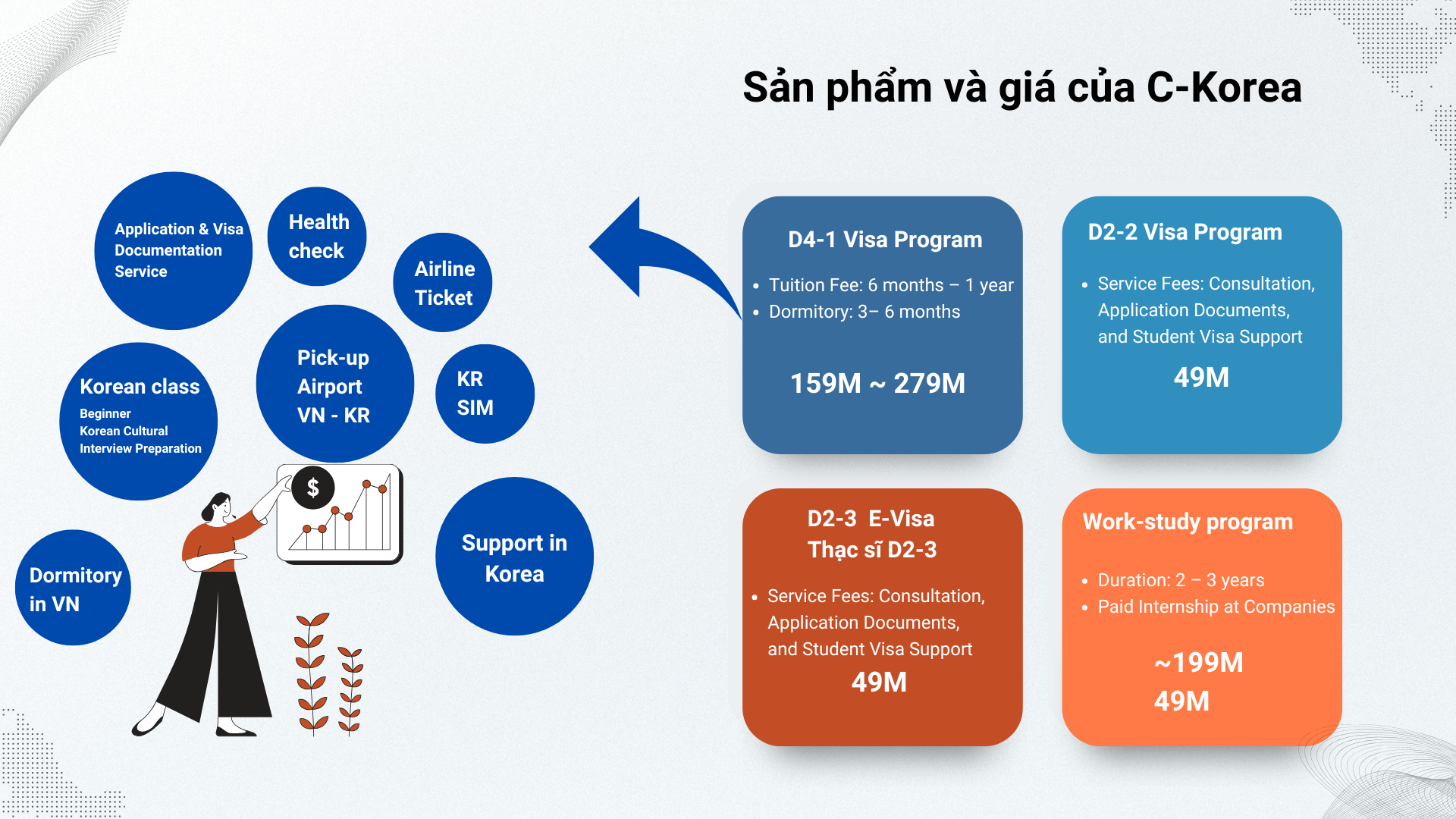
For more information about studying and working in Korea , please contact :
C-KOREA CULTURE AND STUDY ABROAD CONSULTING CO ., LTD.
- Address : 5th Floor , 94-96 Nguyen Van Thuong , Ward 25 , Binh Thanh District , Ho Chi Minh City
- Hotline: +84 28 7308 4247
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61565051012830
- Tiktok: https://www.tiktok.com/@duhoc_ckorea
- Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCQspuqhQlf4IRFCDzN4ce2A